Create Oracle Backup Job in Backup Exec
February 27, 2013 1 Comment
It is very easy to backup Oracle from Backup Exec than Netbackup 🙂 So let’s discuss how to do it.
Some details:
Client Server IP: 10.0.1.100
Client Hostname: orcl_node
Media Server IP: 192.168.1.100
You should have installed RALUS Agent(Backup Exec client software) on client machine, if not see my post “Install Backup Exec Client(Remote Agent) on Linux”(There is also Agent configuration, but we will discuss this configuration in this post also, so just see the client installation section)
1. Configurations on client side
1.1 Oracle user (user that is the oracle software owner) must be in the beoper group.
# id oracle
uid=501(oracle) gid=503(oinstall) groups=503(oinstall),501(asmdba),504(dba),505(oper)# usermod -G asmdba,dba,oper,beoper oracle
# id oracle
uid=501(oracle) gid=503(oinstall) groups=503(oinstall),501(asmdba),504(dba),505(oper),506(beoper)
1.2. Configure RALUS agent on client machine
# /opt/VRTSralus/bin/AgentConfig
Symantec Backup Exec Remote Agent Utility
Choose one of the following options:
1. Configure database access
2. Configure Oracle instance information
3. Quit
Please enter your selection: 1Configuring machine information
Choose one of the following options:
1. Add system credentials for Oracle operations
2. Edit system credentials used for Oracle operations
3. Remove system credentials used for Oracle operations
4. View system credentials used for Oracle operations
5. Quit
Please enter your selection: 1
Enter a user name that has local system credentials: oracle
Enter the password:
Re-enter password:
Validating credentials…….
Do you want to use a custom port to connect to the media server during Oracle operations? (Y/N): N
Commit Oracle operation settings to the configuration file? (Y/N): Y
SUCCESS: Successfully added the entry to the configuration file.Configuring machine information
Choose one of the following options:
1. Add system credentials for Oracle operations
2. Edit system credentials used for Oracle operations
3. Remove system credentials used for Oracle operations
4. View system credentials used for Oracle operations
5. Quit
Please enter your selection: 5Symantec Backup Exec Remote Agent Utility
Choose one of the following options:
1. Configure database access
2. Configure Oracle instance information
3. Quit
Please enter your selection: 2If this computer is a RAC node, you must perform additional steps for configuration before you continue. Refer to the readme for these additional steps.
Configuring the Oracle Agent
Choose one of the following options:
1. Add a new Oracle instance to protect
2. Edit an existing Oracle instance
3. Delete an existing Oracle instance
4. View Oracle instance entries that have been added in the Remote Agent Utility
5. Quit
Please enter your selection: 1
Select an Oracle instance to configure
Entry 1. orcl
Enter the number 0 to go back
Enter your selection: 1
Enter the Oracle database SYSDBA user name: SYS
Enter the Oracle database SYSDBA password:
Re-enter password:
Validating credentials…….
Enter the media server name or IP address: The length of the entered data is greater than the maximum permitted length.
Enter the media server name or IP address: 192.168.1.100
Do you use a recovery catalog? (Y/N):N
Do you want to use a customized job template? (Y/N): N
Commit Oracle operation settings to the configuration file? (Y/N): Y
Created symbolic link for /opt/VRTSralus/bin/libobk.so at /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/db_1/lib/libobk.so
SUCCESS: Successfully added the entry to the configuration file.Configuring the Oracle Agent
Choose one of the following options:
1. Add a new Oracle instance to protect
2. Edit an existing Oracle instance
3. Delete an existing Oracle instance
4. View Oracle instance entries that have been added in the Remote Agent Utility
5. Quit
Please enter your selection: 5Symantec Backup Exec Remote Agent Utility
Choose one of the following options:
1. Configure database access
2. Configure Oracle instance information
3. Quit
Please enter your selection: 3
2. Configurations on media server side
Run Backup Exec from start menu.
2.1 Adding client info.
From the menu bar click Tools->Options
In Job Defaults section –> Oracle –> click button Modify list
Click New button –> again New button –> and again New button
Fill the fields,
Username: oracle
Password:
Confirm Password:
Account Name: oracle
click OK
click OK.
click OK -> click OK –> click OK
2.2 Creating backup job.
From the left pane-> Backup Tasks-> New job
In Source section->Selections
Selection list name: Enter the name you want, let it be Oracle-test
Check View by Resource->All Resources-> Favorite Resources->orcl-node->Oracle Database “orcl”..->Tablespaces
I will not discuss all sections in detail, they are self-explanatory..
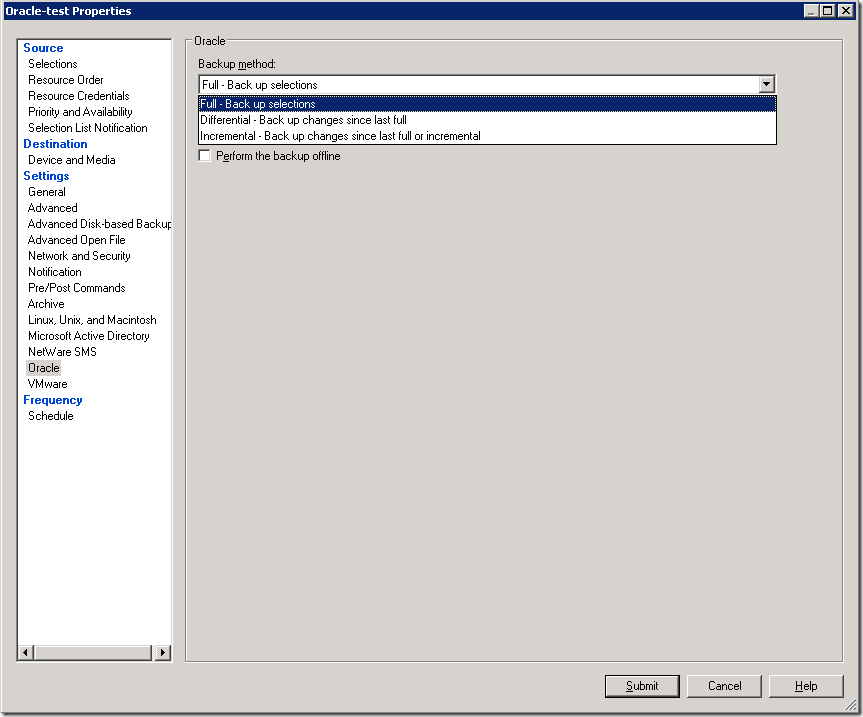
In Settings section-> Oracle –> choose Backup method and other necessary options like Delete backed up archive log files and so on…
By default job will run immediately after clicking the Submit button , but if you want to configure the schedule of your job , do the following:
In Frequency section –>Schedule-> choose Run according to schedule-> click Edit Schedule Details button and choose your appropriate schedule..
For example if you want your backup to run everyday at 1:00AM and no later than 11:00AM, click Day Interval –> check Every and write 1
In Time Window, fill :
Start no earlier than: 1:00AM
and no later than: 11:00AM
Click OK.
Click Submit button.
That’s it.